Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids: What Every Woman Should Know

Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in or on the uterus. Though typically benign, they can sometimes lead to a wide range of uncomfortable symptoms that impact a woman’s daily life and reproductive health. Understanding the symptoms of uterine fibroids is essential for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
In this detailed blog, we will explore the common and uncommon signs of uterine fibroids, their potential complications, when to see a doctor, and frequently asked questions. If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a trusted Gynecologist in Delhi for a proper evaluation.
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
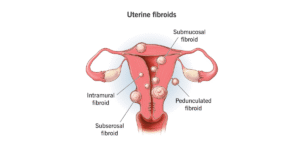
Uterine fibroids, also called leiomyomas or myomas, are growths made up of muscle and fibrous tissue that form on the uterus. These fibroids can range in size from as small as a seed to as large as a melon. Many women may have fibroids without realizing it, as they do not always cause noticeable symptoms.
However, in some cases, fibroids can grow large and cause significant discomfort and complications.
Common Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
Here are the most commonly reported symptoms of uterine fibroids:
1. Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
One of the hallmark signs of fibroids is menorrhagia, or abnormally heavy menstrual bleeding. Women may find themselves soaking through tampons or sanitary pads every hour or passing large blood clots.
2. Pelvic Pain and Pressure
Fibroids can cause a sensation of pressure or fullness in the pelvic area. This may lead to persistent pelvic pain or discomfort, especially during periods.
3. Prolonged Periods
While a normal menstrual cycle lasts about 4 to 7 days, fibroids can extend this duration, leading to periods that last more than a week.
4. Frequent Urination
Large fibroids can press against the bladder, reducing its capacity and causing the need to urinate frequently or urgently, even during the night (nocturia).
5. Constipation or Bloating
When fibroids press on the rectum, they can make bowel movements difficult, leading to constipation. Abdominal bloating and a feeling of fullness are also common.
6. Pain During Intercourse
Some women experience pain or discomfort during sex (dyspareunia), especially if the fibroids are located near the cervix or lower part of the uterus.
7. Lower Back Pain
Larger fibroids that press against the muscles and nerves of the lower back may cause persistent or radiating back pain.
8. Fatigue and Weakness
Chronic blood loss due to heavy periods can lead to iron-deficiency anemia, causing fatigue, shortness of breath, and weakness.
Uncommon or Rare Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
While the above symptoms are the most common, there are some less frequent signs that may also be linked to fibroids:
-
Swelling in the lower abdomen (giving the appearance of pregnancy)
-
Leg pain or swelling (if fibroids press on blood vessels)
-
Infertility or difficulty conceiving
-
Repeated miscarriages
How Are Fibroids Diagnosed?
If you’re experiencing the above symptoms of uterine fibroids, your doctor may recommend:
-
Pelvic Exam: To check for irregularities in the size and shape of the uterus.
-
Ultrasound: The most common imaging test to confirm fibroids.
-
MRI Scan: To evaluate the size, number, and location of fibroids.
-
Hysteroscopy or Sonohysterography: Advanced procedures to visualize the inside of the uterus.
For a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment, consult an experienced Gynecologist in Delhi.
When to See a Doctor?
You should seek medical attention if:
-
Your periods are unusually heavy or prolonged.
-
You experience persistent pelvic pain or pressure.
-
You have difficulty emptying your bladder or bowels.
-
You’re facing infertility or recurrent pregnancy loss.
-
You notice rapid abdominal swelling.
Timely diagnosis and intervention can help manage symptoms effectively and prevent complications.
Complications Caused by Uterine Fibroids
While fibroids are not cancerous, they can lead to:
-
Severe Anemia due to blood loss.
-
Infertility or difficulty carrying a pregnancy to term.
-
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) from bladder pressure.
-
Emotional and mental stress due to chronic symptoms.
-
Impact on quality of life, limiting normal activities.
Treatment Options for Uterine Fibroids
Depending on the severity of symptoms, fibroids can be managed through:
1. Watchful Waiting
If fibroids are small and asymptomatic, monitoring without immediate treatment may be sufficient.
2. Medications
Hormonal treatments like GnRH agonists, oral contraceptives, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) help manage symptoms.
3. Non-Invasive Procedures
-
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE): Blocks blood flow to fibroids, causing them to shrink.
-
MRI-Guided Focused Ultrasound Surgery (FUS): Uses sound waves to destroy fibroids.
4. Surgical Options
-
Myomectomy: Removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus.
-
Hysterectomy: Complete removal of the uterus, usually for severe cases or when fertility is not a concern.
For guidance on the best approach for your condition, consult Dr. Sadhana Gosain, a senior gynecologist and fibroid specialist in Delhi.
About Dr. Sadhana Gosain
Dr. Sadhana Gosain is a renowned Gynecologist in Delhi with over 26 years of experience in gynecology, infertility, and laparoscopic surgery. She specializes in treating complex cases of uterine fibroids, high-risk pregnancies, and hormonal disorders with both surgical and non-surgical approaches.
Her clinic provides personalized care with state-of-the-art technology, ensuring comfort and successful outcomes for women of all ages.

Gynecologist in Delhi
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can fibroids go away on their own?
Small fibroids may shrink or disappear after menopause due to hormonal changes. However, many fibroids persist or grow, especially during reproductive years.
Q2. Do fibroids always cause symptoms?
No. Some women may have fibroids without any symptoms, while others may experience severe discomfort. The symptoms of uterine fibroids vary depending on their size, number, and location.
Q3. Are uterine fibroids cancerous?
Fibroids are almost always non-cancerous (benign). Less than 1% may become cancerous, known as leiomyosarcoma, but this is extremely rare.
Q4. Can I get pregnant if I have fibroids?
Yes, many women with fibroids conceive and carry healthy pregnancies. However, some types of fibroids can interfere with implantation or cause pregnancy complications.
Q5. How are fibroids different from polyps or cysts?
-
Fibroids are muscle tumors inside or outside the uterus.
-
Polyps are overgrowths of the uterine lining.
-
Cysts usually develop on ovaries and are fluid-filled.
Q6. Is surgery the only option for fibroids?
No. Mild cases can be managed with medications or non-invasive procedures. Surgery is reserved for large or symptom-causing fibroids that don’t respond to other treatments.
Q7. How can I prevent uterine fibroids?
There is no guaranteed way to prevent fibroids, but maintaining a healthy weight, managing hormones, and regular gynecological checkups can help reduce risk.
Q8. Can diet affect fibroid growth?
Some studies suggest that high consumption of red meat, alcohol, and processed foods may increase fibroid risk, while green vegetables and vitamin D might offer protective effects.
Q9. Can fibroids come back after treatment?
Yes, especially after myomectomy. Fibroids may regrow if the uterus is left intact. Hysterectomy is the only permanent solution to prevent recurrence.
Q10. Who is the best doctor in Delhi for fibroid treatment?
Dr. Sadhana Gosain is one of the most experienced and trusted gynecologists in Delhi for fibroid treatment, including laparoscopic surgery and fertility-preserving options.
View this post on Instagram
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of uterine fibroids is the first step toward managing this common gynecological issue. Whether you’re facing heavy periods, pelvic pain, or unexplained bloating, don’t ignore these warning signs. Early detection and professional care can greatly improve your quality of life.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s time to consult a reputed Gynecologist in Delhi like Dr. Sadhana Gosain for a personalized diagnosis and expert care.

