Fibroids During Pregnancy: Causes, Risks, Symptoms & Safe Treatment Options

Fibroids During Pregnancy is a common concern for many women, especially those who are planning to conceive or are already expecting. Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus, and while many women with fibroids have normal pregnancies, some may experience complications depending on the size, number, and location of the fibroids.
In this detailed guide, we will explain everything you need to know about fibroids during pregnancy, including causes, symptoms, possible risks, diagnosis, and safe management options to ensure a healthy pregnancy journey.
What Are Fibroids?
Fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas or myomas, are benign (non-cancerous) tumors that grow from the muscular tissue of the uterus. They vary in size—from as small as a seed to as large as a melon—and can be single or multiple.
Fibroids are common in women of reproductive age and often go unnoticed unless they cause symptoms or complications.
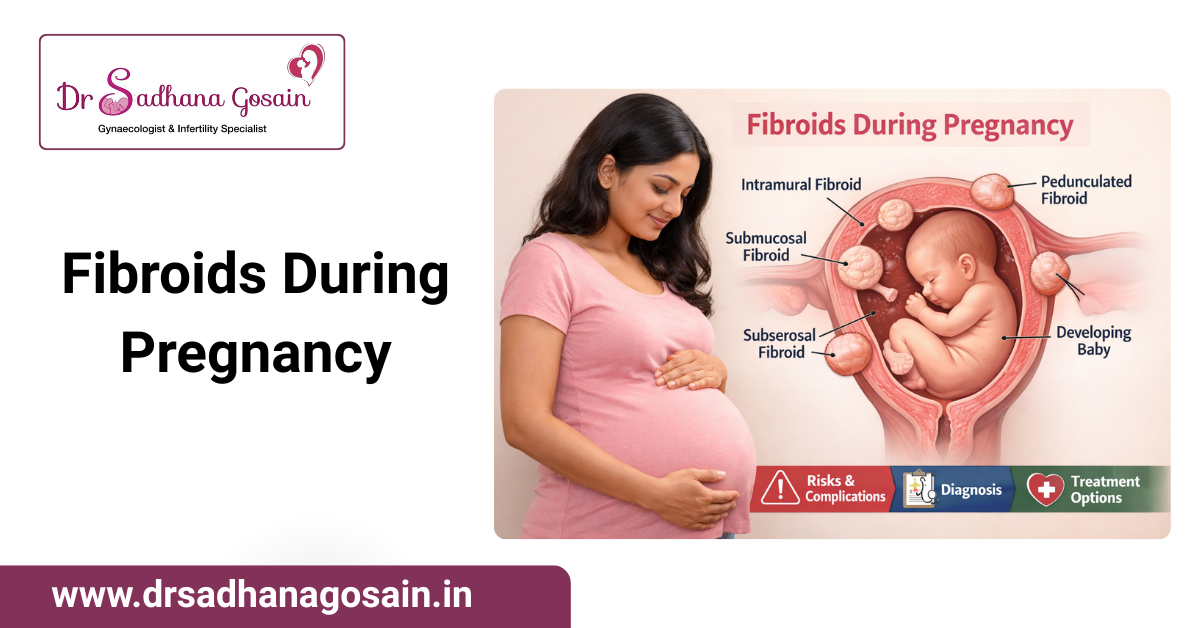
Types of Fibroids That Can Affect Pregnancy
Understanding the type of fibroid is important, as it determines the level of risk during pregnancy:
1. Intramural Fibroids
-
Grow within the muscular wall of the uterus
-
Most common type
-
Can sometimes interfere with implantation or uterine expansion
2. Submucosal Fibroids
-
Grow into the uterine cavity
-
Most likely to affect fertility and pregnancy
-
Can increase the risk of miscarriage
3. Subserosal Fibroids
-
Grow on the outer surface of the uterus
-
Usually cause fewer pregnancy complications
4. Pedunculated Fibroids
-
Attached to the uterus by a stalk
-
Can twist and cause severe pain
Can You Get Pregnant With Fibroids?
Yes, many women conceive and deliver healthy babies despite having fibroids. However, fertility may be affected if fibroids block the fallopian tubes, alter the uterine cavity, or affect blood flow to the uterus.
If you’re planning pregnancy and have fibroids, consulting an experienced gynecologist is essential. Early evaluation helps reduce risks and plan appropriate care.
Fibroids During Pregnancy: Common Symptoms
Symptoms of fibroids during pregnancy may vary. Some women remain completely asymptomatic, while others may experience:
-
Pelvic pain or pressure
-
Lower back pain
-
Frequent urination
-
Constipation
-
Abdominal discomfort
-
Pain during the second or third trimester
-
Sudden sharp pain due to fibroid degeneration
🔹 Red degeneration is a condition where fibroids outgrow their blood supply during pregnancy, causing acute pain and fever.
How Fibroids Change During Pregnancy
Due to increased estrogen and progesterone levels, fibroids may grow during the first trimester. However, studies show that many fibroids remain stable or even shrink in the later stages of pregnancy.
Not all fibroids grow, and growth patterns differ from woman to woman.
Risks of Fibroids During Pregnancy
While most pregnancies progress normally, fibroids during pregnancy can sometimes increase the risk of complications, such as:
1. Miscarriage
-
More common with large or submucosal fibroids
2. Preterm Labor
-
Fibroids can irritate the uterus and trigger early contractions
3. Placental Abruption
-
Placenta may separate prematurely from the uterus
4. Breech Position
-
Fibroids can restrict fetal movement
5. Cesarean Delivery
-
Large fibroids may obstruct the birth canal
6. Postpartum Hemorrhage
-
Fibroids can interfere with uterine contraction after delivery
Diagnosis of Fibroids During Pregnancy
Fibroids are usually diagnosed through:
-
Ultrasound scans (routine pregnancy scans often detect them)
-
MRI (rarely required during pregnancy)
Doctors monitor fibroid size and location regularly to ensure maternal and fetal safety.
Safe Management of Fibroids During Pregnancy
Treatment during pregnancy focuses on symptom relief, not fibroid removal.
1. Conservative Management
-
Bed rest
-
Hydration
-
Pain management with pregnancy-safe medications
2. Pain Control
-
Mild analgesics prescribed by a gynecologist
-
Avoid self-medication
3. Monitoring
-
Regular ultrasounds to track fibroid growth
-
Monitoring fetal development
⚠️ Surgery (myomectomy) is generally avoided during pregnancy unless there is a life-threatening complication.
Delivery Options With Fibroids
The mode of delivery depends on:
-
Fibroid size
-
Location
-
Obstruction of the cervix
-
Baby’s position
Many women with fibroids can have a normal vaginal delivery, while others may require a planned C-section.
When Should You See a Gynecologist?
You should consult a specialist immediately if you experience:
-
Severe abdominal pain
-
Vaginal bleeding
-
Fever with pain
-
Reduced fetal movements
For expert care and personalized pregnancy management, consulting the Best Gynecologist in Karol Bagh can help ensure both maternal and fetal well-being through accurate diagnosis and evidence-based treatment.
Can Fibroids Affect the Baby?
In most cases, fibroids do not directly harm the baby. However, indirect effects like reduced space in the uterus or placental issues may influence fetal growth, making regular monitoring essential.
Tips for a Healthy Pregnancy With Fibroids
-
Attend all prenatal appointments
-
Follow doctor-recommended activity levels
-
Maintain a healthy, fiber-rich diet
-
Stay hydrated
-
Manage stress
-
Avoid heavy lifting
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Are fibroids dangerous during pregnancy?
Not always. Most fibroids do not cause serious problems, but regular monitoring is necessary.
Can fibroids shrink after pregnancy?
Yes, fibroids often shrink after delivery due to hormonal changes.
Is bed rest necessary?
Only if advised by your doctor due to pain or complications.
Can fibroids be removed after delivery?
Yes, treatment options like myomectomy can be planned postpartum if needed.
Conclusion
Fibroids during pregnancy may sound concerning, but with early diagnosis, expert guidance, and regular monitoring, most women experience healthy pregnancies and safe deliveries. The key lies in personalized care, understanding risk factors, and timely medical support.
If you are pregnant or planning pregnancy and have fibroids, seeking care from an experienced specialist like the Best Gynecologist in Karol Bagh can make a significant difference in ensuring a smooth and stress-free journey to motherhood.

